In the age of digital transformation, the term “cloud computing” is unavoidable. It powers everything from your morning email to global e-commerce platforms. But scratch the surface, and you’ll find a dizzying array of options, often encapsulated by three acronyms: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
These three cloud delivery models form the fundamental layers of the modern computing world. Making the wrong choice can lead to wasted budget, poor performance, and unnecessary complexity. The right choice, however, can unlock enormous scalability and flexibility, while simultaneously reducing your Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
This comprehensive guide will break down the crucial differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, detailing who manages what, providing real-world examples, and helping you determine the best model for your business needs.
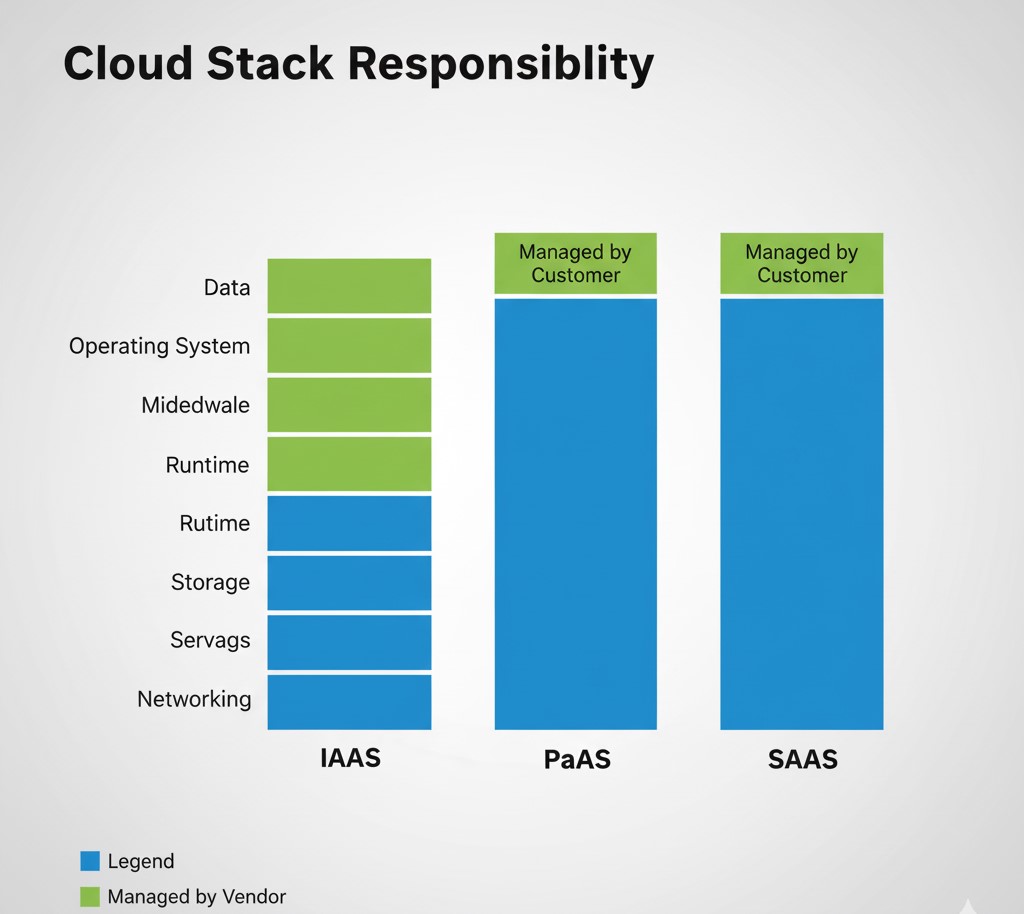
Understanding the Cloud Continuum: Where Does the Responsibility Lie?
The most critical factor distinguishing the three cloud service models is the level of control and management responsibility retained by the customer versus the provider.
To grasp this concept easily, imagine your IT infrastructure as a restaurant meal.
| Scenario | On-Premises (Traditional IT) | IaaS | PaaS | SaaS |
| Analogy | Cooking at Home | Ordering Takeout | Ordering a Meal Kit | Dining Out (All-Inclusive) |
| You Manage | Everything (Food, kitchen, cleanup, table) | The Food (App/Data, OS, Middleware) | The Recipe/Toppings (App/Data) | Only the Eating (Data use) |
| Vendor Manages | Nothing | The Kitchen (Servers, Storage, Network) | The Kitchen & Ingredients (OS, Servers, Runtime) | Everything (The entire meal, service, and venue) |
This responsibility model highlights the spectrum: IaaS offers maximum control but requires more management, while SaaS offers maximum convenience with minimal control.
1. Software as a Service (SaaS): The Finished Product
SaaS is the simplest and most widely adopted cloud computing category. It delivers a fully-fledged software application over the internet on a subscription basis.
- What it is: The software application itself. Users access it via a web browser or mobile app.
- Customer Role: You only manage your usage and the data you input. You don’t manage the application code, the underlying hardware, or maintenance.
- Core Benefit: Speed and simplicity. You get immediate value with minimal setup.
- Examples: Google Workspace (Gmail, Docs), Salesforce (CRM), Microsoft 365, Slack, Dropbox.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS): The Development Environment
PaaS provides developers with a complete, ready-to-use environment for developing, running, and managing applications. It strips away the burden of infrastructure management, allowing teams to focus purely on coding and application logic.
- What it is: An application development platform and framework.
- Customer Role: You manage your application code and the data. The provider manages everything else, including the operating systems, runtime, servers, and patching. This greatly enhances Agile development and DevOps practices.
- Core Benefit: Velocity. It accelerates time-to-market for new applications.
- Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): The Building Blocks
IaaS is the foundational layer of the cloud. It gives you access to the basic computing resources you would typically find in a data center, but delivered virtually and on-demand.
- What it is: Virtualized hardware resources, including virtual machines (VMs), storage, and networking capabilities.
- Customer Role: You have the most control here. You must manage the Operating System (OS), middleware, runtime environments, application, and data.
- Core Benefit: Maximum control and customization. Ideal for companies with highly specific security, compliance, or legacy system requirements.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS EC2), Google Compute Engine (GCE), Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
Detailed Comparison: Pros, Cons, and Key Trade-Offs
Choosing the right cloud service model is a trade-off between control and complexity. Here is a side-by-side analysis of how the three stack up across critical decision factors.
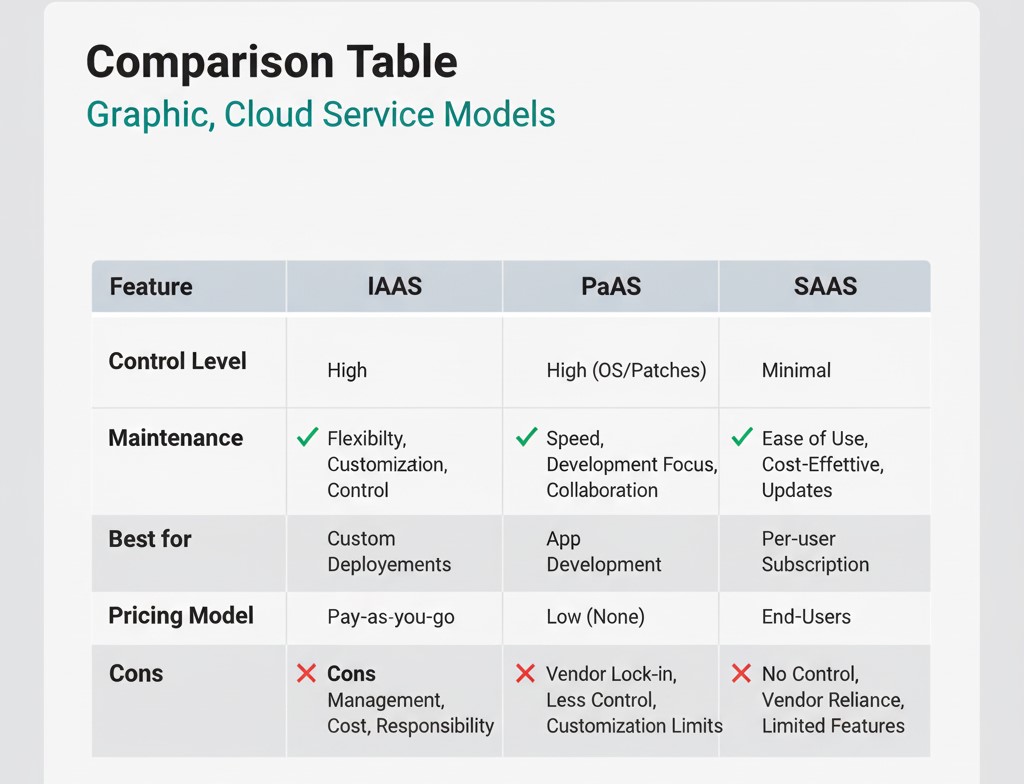
| Feature | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Software as a Service (SaaS) |
| Primary User | IT Architects, System Admins, Developers | Developers, Software Teams | End-Users, General Business Teams |
| Control Level | High (Full OS and network control) | Moderate (Control over application and code) | Minimal (Control over data/settings) |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go (Consumption-based) | Subscription or Usage-based (Resources consumed) | Per-user subscription (Fixed monthly cost) |
| Flexibility | Highest (Can run any OS or software) | High (Supports multiple programming languages) | Lowest (Limited to vendor features) |
| Key Advantage | Unmatched flexibility and customizability | Fast deployment and lower development costs | Maximum convenience and ease of use |
| Key Disadvantage | Highest management burden; potential for unchecked cloud cost | Potential vendor lock-in; platform customization limits | Low control over features, security, and updates |
IaaS: The Flexibility vs. Complexity Trade-Off
IaaS is the foundational layer for multicloud migration and the deployment of new, complex systems. It’s perfect for enterprises performing a “lift and shift” of existing on-premises systems, as it allows them to replicate their familiar virtualized environment without the need to buy and maintain physical servers.
- Pros: Complete control over your infrastructure, easily supports hybrid cloud strategies, highly scalable resources (up or down).
- Cons: You are responsible for security settings, patching the OS, and managing licenses—higher management overhead.
PaaS: The Velocity vs. Vendor Lock-in Trade-Off
PaaS is a huge win for companies that prioritize rapid application development (RAD). By automating away the “undifferentiated heavy lifting” of managing servers and operating systems, developers can achieve greater development velocity.
- Pros: Streamlined workflows, built-in scaling, and deployment tools for CI/CD pipelines.
- Cons: Limited customization below the application layer, and the frameworks offered may lead to vendor lock-in, making migration to a different platform difficult.
SaaS: The Convenience vs. Customization Trade-Off
For small businesses and large corporations alike, SaaS is the default choice for business-critical but non-core functions. It’s the fastest and easiest path to getting a tool running.
- Pros: Zero installation, minimal IT staffing needed, predictable monthly costs, and automatic security updates.
- Cons: Limited ability to customize the software’s look, feel, or function; complete reliance on the vendor for uptime and data security.
When to Choose Which Model: Use Cases for Business Success
The decision of when to use IaaS PaaS or SaaS hinges on your organization’s technical skill, budget, and need for control.
The IaaS User: The Customizer
Choose IaaS if your priority is control and customization.
- Disaster Recovery: Setting up highly available, scalable backup and recovery solutions that mirror your on-premises systems.
- Web Hosting: Running custom, mission-critical web applications that require a specific OS or configuration.
- Big Data Analytics: Needing massive, scalable compute resources for short bursts of data processing, paid for on a pay-as-you-go basis.
The PaaS User: The Developer
Choose PaaS if your goal is development speed and deployment efficiency.
- Microservices and APIs: Building modular, containerized applications where the platform handles the scaling and orchestration.
- Rapid Prototyping: Development teams can launch new versions and test environments in minutes instead of weeks.
- IoT/Mobile Backends: Needing a managed platform to handle complex data streams from thousands of devices without building the server infrastructure from scratch.
The SaaS User: The End-User
Choose SaaS if your requirement is ready-to-use software for immediate functionality.
- Internal Collaboration: Providing employees with standardized tools for communication and documentation (e.g., email, file sharing).
- Sales/Marketing: Utilizing specialized CRM software and marketing automation without any infrastructure hassle.
- Startups: Needing enterprise-level tools quickly and cheaply without a dedicated IT team.
Optimizing Your Cloud Budget
Regardless of which cloud service model you adopt—or more likely, the blend of all three that makes up your IT portfolio—managing the cost efficiently is paramount. The elasticity and pay-as-you-go nature of the cloud can lead to uncontrolled spending if not monitored closely.
To help you navigate the complexity of cloud pricing, licenses, and finding the best possible technology deals for your business, we highly recommend checking out the curated offers at offerlooters.com. They provide the resources and insights necessary to ensure you are maximizing the value of your IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS investments, ensuring you get the full benefits of cloud computing without the budgetary surprises.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can a company use IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS simultaneously?
A: Yes, absolutely. The vast majority of modern enterprises adopt a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy, utilizing a mix of all three models. For example, a company might use IaaS for their custom backend server, PaaS for their internal mobile application development environment, and SaaS for their employee email and payroll systems. This allows them to balance control, development speed, and ease of use.
Q2: What is the primary difference in security responsibility across the models?
A: Security is a shared responsibility in the cloud, but the scope changes dramatically.
- IaaS: The user is largely responsible for the security in the cloud (OS security, patching, application security).
- PaaS: The responsibility is more shared. The provider secures the platform and OS, while the user secures their application code and data.
- SaaS: The provider takes nearly all the security burden, only leaving the user responsible for access control and their own data.
Q3: Which cloud model is the most cost-effective for a startup?
A: SaaS is often the most cost-effective for a lean startup, especially for non-core functions like email, accounting, and CRM, because it eliminates all capital expenditure and infrastructure management overhead. However, if the startup is building a custom application, PaaS offers the best balance, significantly reducing the cost and time involved in deployment and infrastructure configuration.
Conclusion: The Right Cloud for the Right Job
The conversation around IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS isn’t about finding a single “best” solution; it’s about understanding the specific tools for your unique IT job.
- If your team needs full control and customization of the operating system for a complex, customized workload, IaaS is your starting point.
- If your developers need to accelerate application deployment and focus solely on writing code, PaaS is your platform.
- If your end-users need a ready-to-go business tool with minimal management, SaaS is the simple answer.
By understanding the cloud stack layers and the crucial handoff of vendor management, you can make smarter strategic decisions that optimize your IT resources, accelerate your digital products, and ensure your business is built on a resilient, scalable foundation.
Ready to find the ideal technology resources for your chosen cloud model? I can help you research the leading providers for any of the three models—AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, Heroku, Salesforce, and more.